Kubectl MCP Tool
Kubectl MCP Tool — это сервер протокола Model Context Protocol (MCP) для Kubernetes, который позволяет AI-ассистентам взаимодействовать с кластерами Kubernetes на естественном языке.
Kubectl MCP Server
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for Kubernetes that enables AI assistants like Claude, Cursor, and others to interact with Kubernetes clusters through natural language.
🎥 Live Demo - Watch kubectl-mcp-tool in Action with Claude!
🎥 Live Demo - Watch kubectl-mcp-tool in Action with Cursor!
🎥 Live Demo - Watch kubectl-mcp-tool in Action with Windsurf!
Features
Core Kubernetes Operations
- [x] Connect to a Kubernetes cluster
- [x] List and manage pods, services, deployments, and nodes
- [x] Create, delete, and describe pods and other resources
- [x] Get pod logs and Kubernetes events
- [x] Support for Helm v3 operations (installation, upgrades, uninstallation)
- [x] kubectl explain and api-resources support
- [x] Choose namespace for next commands (memory persistence)
- [x] Port forward to pods
- [x] Scale deployments and statefulsets
- [x] Execute commands in containers
- [x] Manage ConfigMaps and Secrets
- [x] Rollback deployments to previous versions
- [x] Ingress and NetworkPolicy management
- [x] Context switching between clusters
Natural Language Processing
- [x] Process natural language queries for kubectl operations
- [x] Context-aware commands with memory of previous operations
- [x] Human-friendly explanations of Kubernetes concepts
- [x] Intelligent command construction from intent
- [x] Fallback to kubectl when specialized tools aren't available
- [x] Mock data support for offline/testing scenarios
- [x] Namespace-aware query handling
Monitoring
- [x] Cluster health monitoring
- [x] Resource utilization tracking
- [x] Pod status and health checks
- [x] Event monitoring and alerting
- [x] Node capacity and allocation analysis
- [x] Historical performance tracking
- [x] Resource usage statistics via kubectl top
- [x] Container readiness and liveness tracking
Security
- [x] RBAC validation and verification
- [x] Security context auditing
- [x] Secure connections to Kubernetes API
- [x] Credentials management
- [x] Network policy assessment
- [x] Container security scanning
- [x] Security best practices enforcement
- [x] Role and ClusterRole management
- [x] ServiceAccount creation and binding
- [x] PodSecurityPolicy analysis
- [x] RBAC permissions auditing
- [x] Security context validation
Diagnostics
- [x] Cluster diagnostics and troubleshooting
- [x] Configuration validation
- [x] Error analysis and recovery suggestions
- [x] Connection status monitoring
- [x] Log analysis and pattern detection
- [x] Resource constraint identification
- [x] Pod health check diagnostics
- [x] Common error pattern identification
- [x] Resource validation for misconfigurations
- [x] Detailed liveness and readiness probe validation
Advanced Features
- [x] Multiple transport protocols support (stdio, SSE)
- [x] Integration with multiple AI assistants
- [x] Extensible tool framework
- [x] Custom resource definition support
- [x] Cross-namespace operations
- [x] Batch operations on multiple resources
- [x] Intelligent resource relationship mapping
- [x] Error explanation with recovery suggestions
- [x] Volume management and identification
Architecture
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Integration
The Kubectl MCP Tool implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling AI assistants to interact with Kubernetes clusters through a standardized interface. The architecture consists of:
- MCP Server: A compliant server that handles requests from MCP clients (AI assistants)
- Tools Registry: Registers Kubernetes operations as MCP tools with schemas
- Transport Layer: Supports stdio, SSE, and HTTP transport methods
- Core Operations: Translates tool calls to Kubernetes API operations
- Response Formatter: Converts Kubernetes responses to MCP-compliant responses
Request Flow
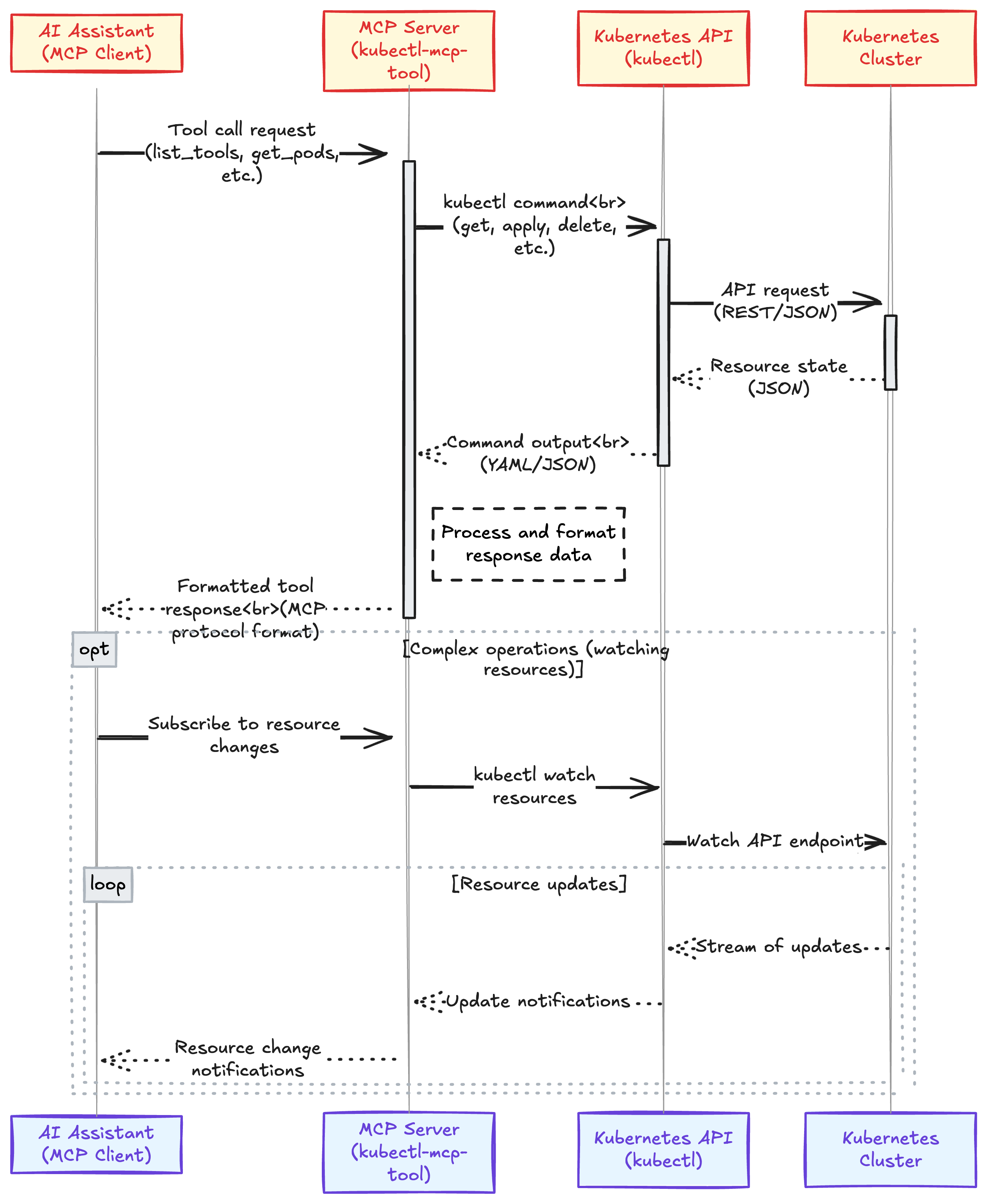
Dual Mode Operation
The tool operates in two modes:
- CLI Mode: Direct command-line interface for executing Kubernetes operations
- Server Mode: Running as an MCP server to handle requests from AI assistants
Installation
For detailed installation instructions, please see the Installation Guide.
You can install kubectl-mcp-tool directly from PyPI:
pip install kubectl-mcp-tool
For a specific version:
pip install kubectl-mcp-tool==1.1.1
The package is available on PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/kubectl-mcp-tool/1.1.1/
Prerequisites
- Python 3.9+
- kubectl CLI installed and configured
- Access to a Kubernetes cluster
- pip (Python package manager)
Global Installation
# Install latest version from PyPI
pip install kubectl-mcp-tool
# Or install development version from GitHub
pip install git+https://github.com/rohitg00/kubectl-mcp-server.git
Local Development Installation
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/rohitg00/kubectl-mcp-server.git
cd kubectl-mcp-server
# Install in development mode
pip install -e .
Verifying Installation
After installation, verify the tool is working correctly:
kubectl-mcp --help
Note: This tool is designed to work as an MCP server that AI assistants connect to, not as a direct kubectl replacement. The primary command available is kubectl-mcp serve which starts the MCP server.
Docker Image
If you prefer using Docker, a pre-built image is available on Docker Hub:
# Pull the latest image
docker pull rohitghumare64/kubectl-mcp-server:latest
Running the image
The server inside the container listens on port 8000. Bind any free host port to 8000 and mount your kubeconfig:
# Replace 8081 with any free port on your host
# Mount your local ~/.kube directory for cluster credentials
docker run -p 8081:8000 \
-v $HOME/.kube:/root/.kube \
rohitghumare64/kubectl-mcp-server:latest
-p 8081:8000maps host port 8081 → container port 8000.-v $HOME/.kube:/root/.kubemounts your kubeconfig so the server can reach the cluster.
Building a multi-architecture image (AMD64 & ARM64)
If you want to build and push a multi-arch image (so it runs on both x86_64 and Apple Silicon), use Docker Buildx:
# Ensure Buildx and QEMU are installed once per machine
# docker buildx create --name multiarch --use
# docker buildx inspect --bootstrap
# Build and push for linux/amd64 and linux/arm64
# (replace <your_username> if you're publishing to your own registry)
docker buildx build \
--platform linux/amd64,linux/arm64 \
-t rohitghumare64/kubectl-mcp-server:latest \
--push .
The published image will contain a manifest list with both architectures, and Docker will automatically pull the correct variant on each machine.
Configuration
The MCP server is allowed to access these paths to read your Kubernetes configuration:
run:
volumes:
- '{{kubectl-mcp-server.kubeconfig}}:/root/.kube'
config:
description: The MCP server is allowed to access this path
parameters:
type: object
properties:
kubeconfig:
type: string
default:
$HOME/.kube
required:
- kubeconfig
This configuration allows users to add their kubeconfig directory to the container, enabling the MCP server to authenticate with their Kubernetes cluster.
Usage with AI Assistants
Using the MCP Server
The MCP Server (kubectl_mcp_tool.mcp_server) is a robust implementation built on the FastMCP SDK that provides enhanced compatibility across different AI assistants:
Note: If you encounter any errors with the MCP Server implementation, you can fall back to using the minimal wrapper by replacing
kubectl_mcp_tool.mcp_serverwithkubectl_mcp_tool.minimal_wrapperin your configuration. The minimal wrapper provides basic capabilities with simpler implementation.
-
Direct Configuration
{ "mcpServers": { "kubernetes": { "command": "python", "args": ["-m", "kubectl_mcp_tool.mcp_server"], "env": { "KUBECONFIG": "/path/to/your/.kube/config", "PATH": "/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin", "MCP_LOG_FILE": "/path/to/logs/debug.log", "MCP_DEBUG": "1" } } } } -
Key Environment Variables
MCP_LOG_FILE: Path to log file (recommended to avoid stdout pollution)MCP_DEBUG: Set to "1" for verbose loggingMCP_TEST_MOCK_MODE: Set to "1" to use mock data instead of real clusterKUBECONFIG: Path to your Kubernetes config fileKUBECTL_MCP_LOG_LEVEL: Set to "DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", or "ERROR"
-
Testing the MCP Server You can test if the server is working correctly with:
python -m kubectl_mcp_tool.simple_pingThis will attempt to connect to the server and execute a ping command.
Alternatively, you can directly run the server with:
python -m kubectl_mcp_tool
Claude Desktop
Add the following to your Claude Desktop configuration at ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json (Windows: %APPDATA%\Claude\mcp.json):
{
"mcpServers": {
"kubernetes": {
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "kubectl_mcp_tool.mcp_server"],
"env": {
"KUBECONFIG": "$HOME/.kube/config" // or whatever your path is for the config file
}
}
}
}
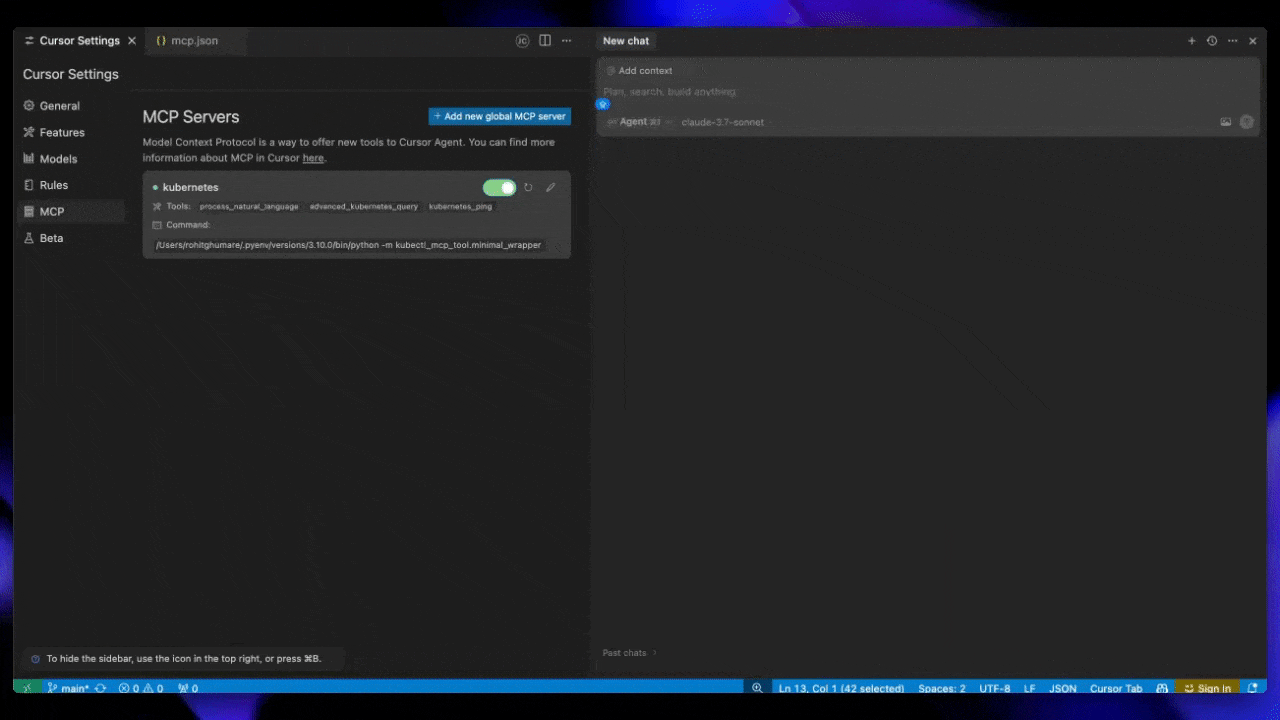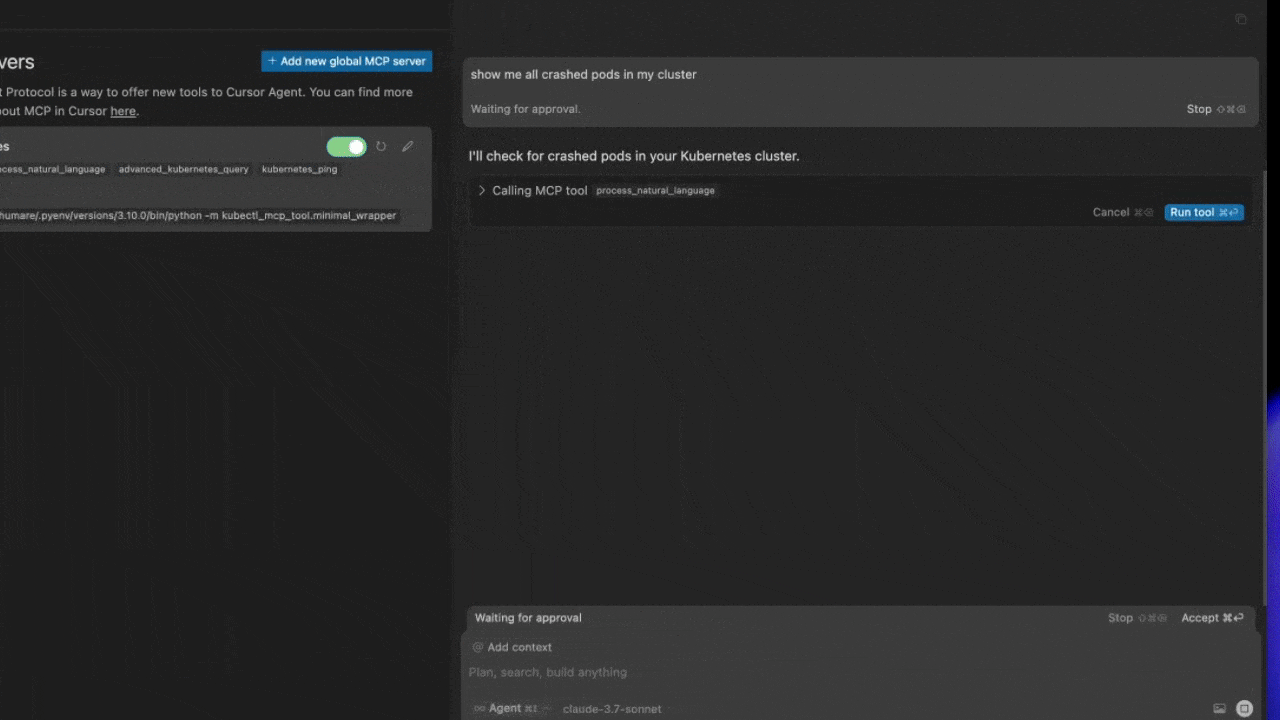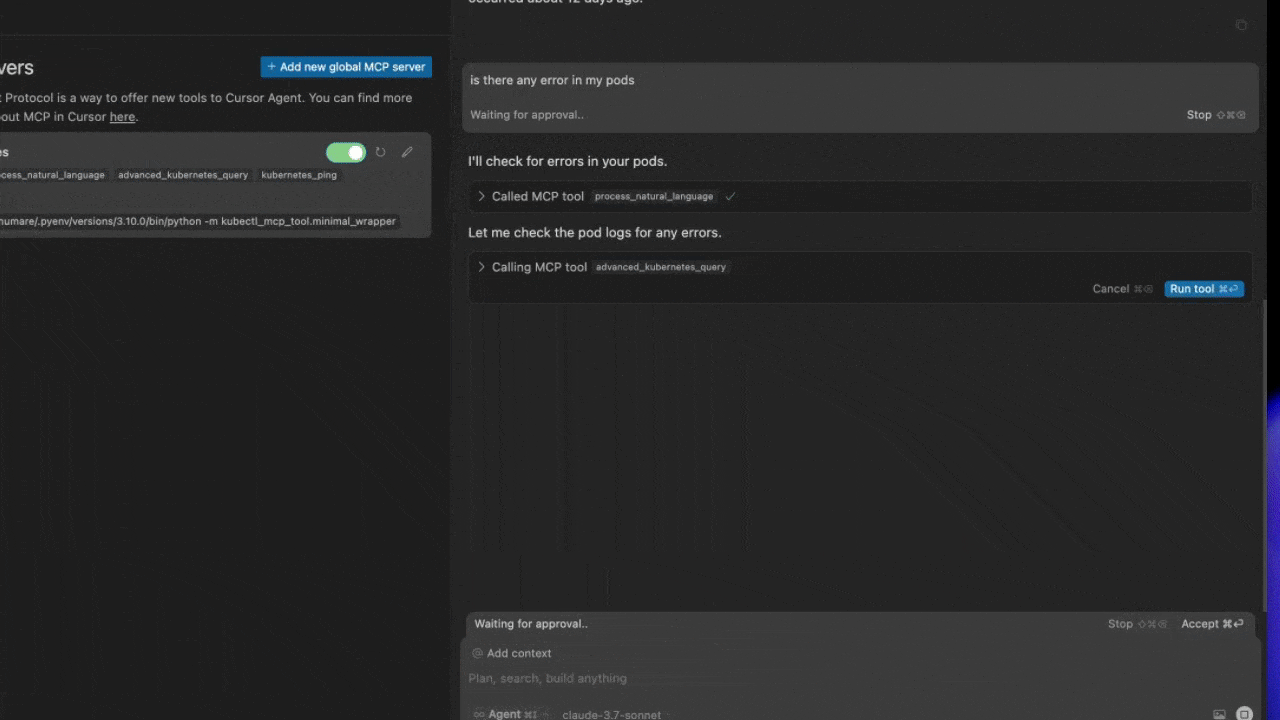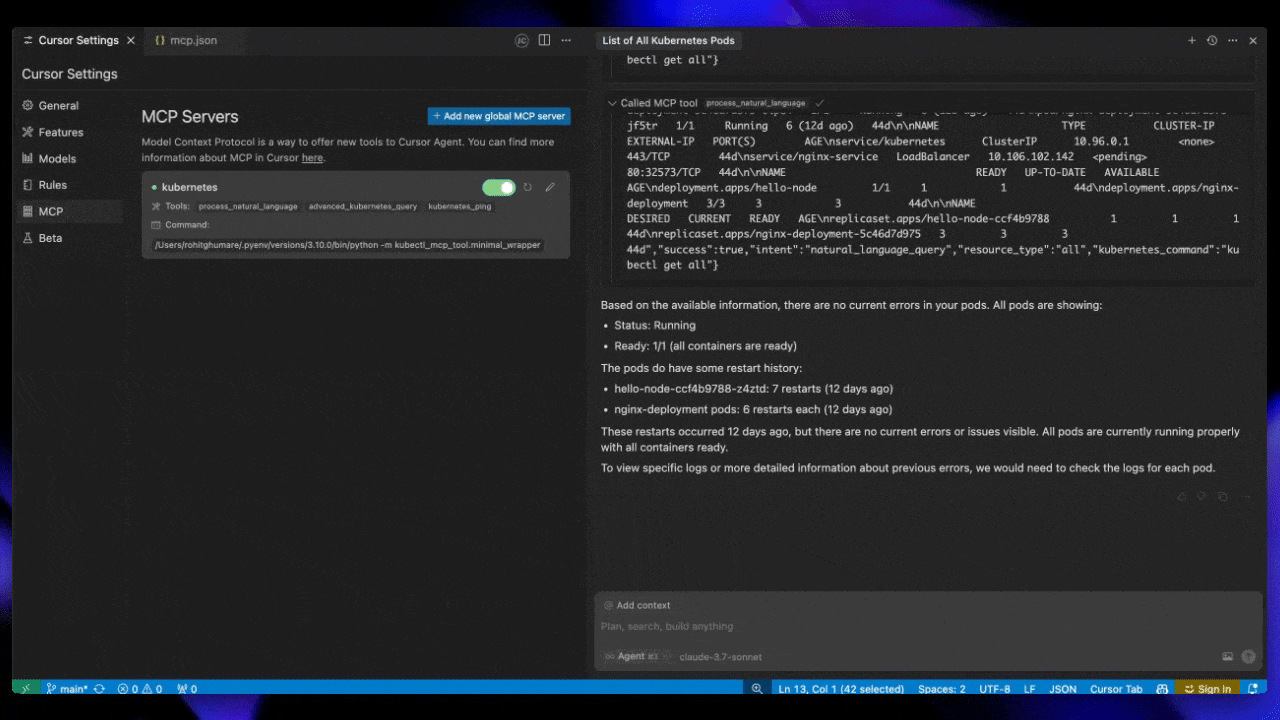
Cursor AI
Add the following to your Cursor AI settings under MCP by adding a new global MCP server:
{
"mcpServers": {
"kubernetes": {
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "kubectl_mcp_tool.mcp_server"],
"env": {
"KUBECONFIG": "/path/to/your/.kube/config",
"PATH": "/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/opt/homebrew/bin"
}
}
}
}
Save this configuration to ~/.cursor/mcp.json for global settings.
Note: Replace
/path/to/your/.kube/configwith the actual path to your kubeconfig file. On most systems, this is~/.kube/config.
Windsurf
Add the following to your Windsurf configuration at ~/.config/windsurf/mcp.json (Windows: %APPDATA%\WindSurf\mcp.json):
{
"mcpServers": {
"kubernetes": {
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "kubectl_mcp_tool.mcp_server"],
"env": {
"KUBECONFIG": "/path/to/your/.kube/config"
}
}
}
}
Automatic Configuration
For automatic configuration of all supported AI assistants, run the provided installation script:
bash install.sh



